 |
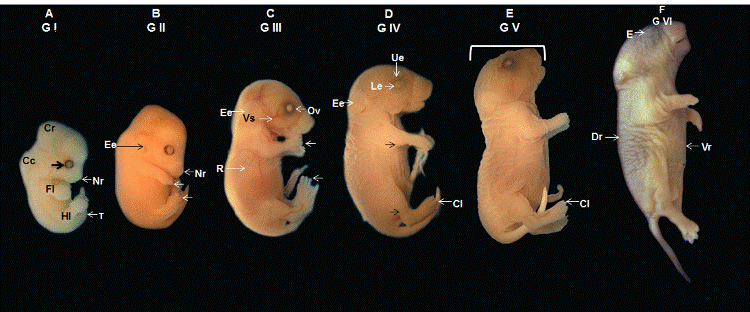
| Figure 1: Macroscopic view of an embryo with a 9-m crown-rump distance. A Cephalic region (Cr), very prominent cervical curvature (Cc), pigmented optic vesicle (Arrow), and nasal region (Nr). The ends of the forelimb (Fl) and hindlimb (Hl) form the shape of a “paddle”. Note the beginning of digit differentiation and slightly pronounced tail (T). B An embryo with a CR distance of 10 mm. Note the forming external ear (Ee), ear canal covered by the pinna, longer Nasal region (Nr), and forelimbs and hindlimbs (Arrows) with differentiated extremities where deeper grooves are visible between the digits. C View of a fetus with a CR distance of 18 mm. The external ear (Ee) and pinna completely cover the ear canal. The vascularization (Vs) is visible over the fetus’ body due to little skin pigmentation. Also note the optic vesicle (Ov) and impression of the ribs (R). Fully separated digits with pronounced claws are visible at the ends of the forelimbs and hindlimbs (Arrows). D A fetus with a CR distance of 20 mm. Note the upper eyelid (Ue) and lower eyelid (Le) covering the eye, further projected external ear (Ee), longer forelimbs and hindlimbs (Arrows) with more pronounced claws (Cl) on the ends. E Fetus with a CR distance of 27 mm. Note the longer oral cavity and nasal region. F Full-term fetus with a CR distance of 30 mm. There is a marked change in skin pigmentation, with a darker dorsal region (Dr) and lighter ventral region (Vr). The open oral cavity and eyes (E) covered by the eyelids can be observed. |