 |
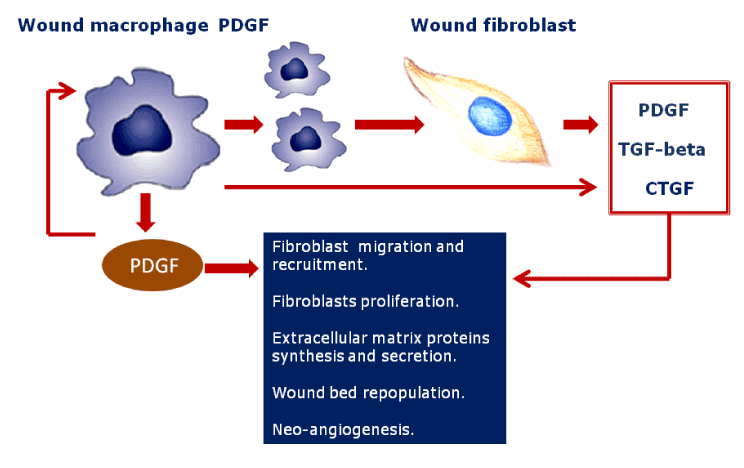
| Figure 2: PDGF signal amplification through infiltrated macrophages. As described elsewhere for tumors, infiltrated macrophages plays an important role in wound healing. PDGF is one of the few growth factors distinguished by the ability to recruit monocytes/macrophages to the wound bed. PDGF protein expression is further amplified by macrophages while more cells are attracted and homed. Via this propagating cross-talk, PDGF stimulates a number of physiological activities on fibroblasts, myofibroblasts, and endothelial cells, thus favoring granulation tissue growth and wound cellularization. PDGF enhances its own secretion by wound fibroblasts as to synthesize other pro-fibrogenic growth factors which in the form of cocktail enhances wound bed granulation, contraction and vascularization. |