 |
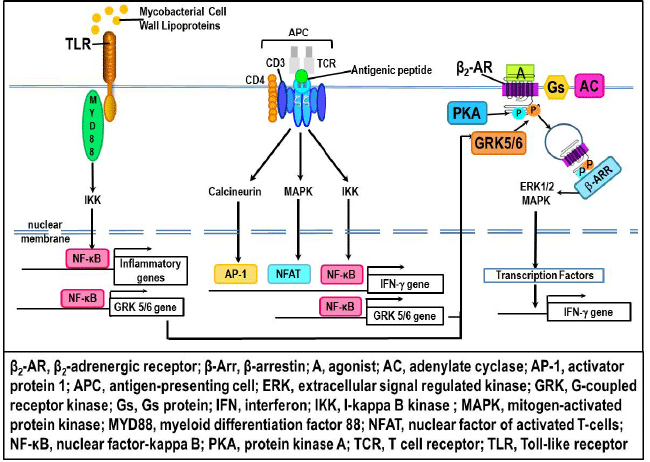
| Figure 19: Proposed mechanism for “switching” β2-AR signaling in draining lymph node cells. Toll-like receptors activated by mycobacterial cell wall lipoprotein and activation of T cell receptors (TCR) in T cells activate the NF-κB signaling pathway. NF-κB is well known to promote gene transcription of IFN-γ. More recently, an NF-κB site was discovered in the promoter region of the GRK 5 and GRK 6 genes. We propose that production of NF-κB, as a result of TLRs and TCR activation, increases production of GRK 5/6. GRK5/6 along with PKA then phosphorylates, which results in a shift in β2-AR signaling from cAMP-PKA towards the ERK1/2 pathway. This shift in signaling by the β2-AR then increases production of IFN-γ. |