 |
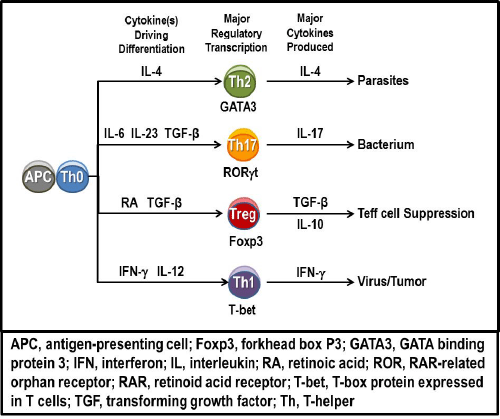
| Figure 6: Th0 cell differentiation. CD4+ T-helper (Th) cell differentiation from naïve CD4+ Th cells activated by antigen-presenting cells (APCs). In response to different pathogens or abnormal host cells, APCs present pathogen/tissue specific antigens to Th0 cells that then induce a biased differentiation into functional Th cells with specific phenotypes. The dominant Th cell subtype that develops is dependent upon the cytokine milieu produced by the APCs and naïve/activated Th cells. Differentiation of each Th cell subset results from the induction of uniquely subset-specific transcriptional programs, as indicated and described in the text. The different Th cell subtypes that differentiate from naïve Th0 cells, their hallmark transcription factor that is expressed and production a specific cytokine profiles characteristic for each subtype is indicated. Also shown is the regulation of Treg cells via TGF-β and IL-6 on Th1:Th17 balance critical for self-tolerance necessary to prevent autoimmunity. |