 |
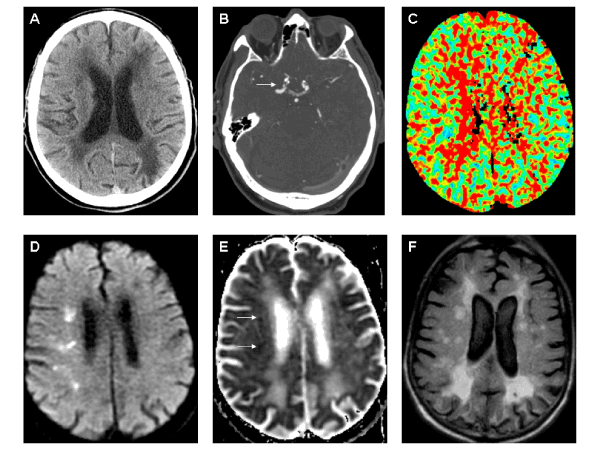
| Figure 1: A. Non-contrast computed tomography (CT) scan showed bilateral periventricular and subcortical hypodensities suggestive of remote small vessel ischemia. An ill-defined right frontal subcortical hypodensity and an old left posterior parietal infarct were also appreciated. B. CT angiography identified bilateral right greater than left supraclinoid calcified plaque with moderate to severe right-sided stenosis (white arrow). C. CT perfusion scan showed prolonged mean transit time and mild increased cerebral blood volume (not shown) in the right subcortical middle cerebral artery territory. D-E. Diffusion weighted imaging and apparent diffusion coefficient scans showed restricted diffusion (arrows) in right subcortical fronto-parietal regions. F. Axial fluid attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) imaging revealed bihemispheric periventricular and subcortical increased signal, diffuse sulcal widening with mild global atrophy, associated encephalomalacia in left posterior parietal region, and right subcortical increased signal corresponding to some of the restricted diffusion sites. Note: all images displayed using radiographic convention. |