 |
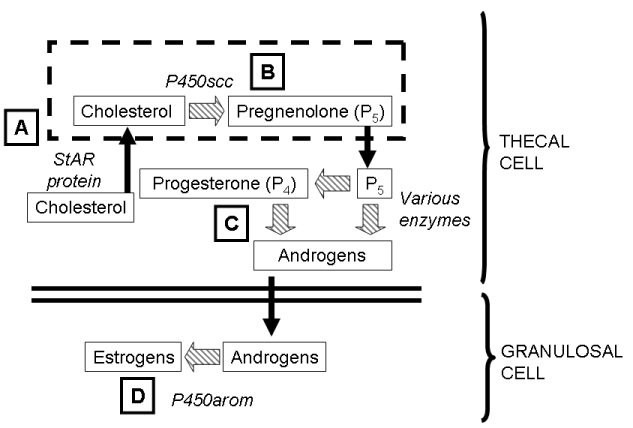
| Figure 1: Schematic outline of the major components of ovarian steroidogenesis considered as possible sites of action of cortisol in the present study. The numbers in circles indicate the sites of specific investigation. 1. The transport of cholesterol from the cytoplasm of the thecal cells into the mitochondria (shown as box with dotted outline, by the involvement of the steroidogenic acute regulatory protein transporter. 2. The conversion within the mitochondria of cholesterol to pregnenolone (P5) by the enzyme P450 side change cleavage (P450scc). 3. The multi-enzyme systems associated with the smooth endoplasmic reticulum of the thecal cells that convert P5 by several stages into androgenic steroid. 4. The aromatization of androgenic steroids by the enzyme P450 aromatase (P450arom) to form estrogenic steroids, principally 17β-estradiol (E2) and estrone (E1). |