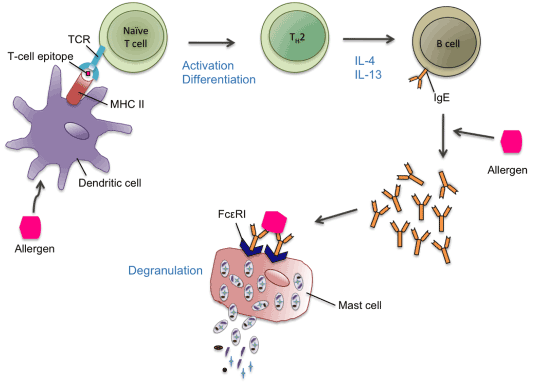
Upon exposure to the allergen, the APCs uptake the allergen and process it. Allergen-derived peptides are presented through MHC class II molecule to naïve T cells, which are then activated and differentiated into Th2. The release of cytokines such as IL-4 and IL-13 from Th2 causes a class switch in B cells to produce allergen-specific IgE antibodies. Upon second exposure to the same allergen, IgE are massively produced, cross-link with the allergen and FcεRI on mast cells and induce degranulation. Release of mediators such as histamine and leukotriene results in inflammation and other associated immediate anaphylactic responses.