 |
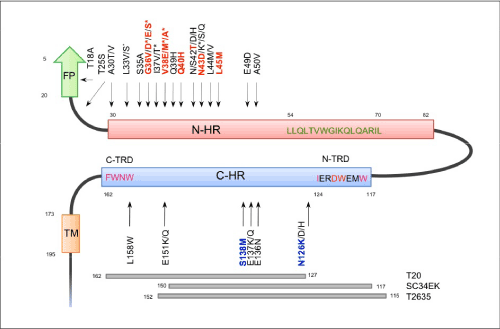
| Figure 7: Schematic view of HIV-1 gp41 functional domains and mutation map for T-20. Putative hydrophobic pocket region of the N-HR is shown (green) and may form a leucine-zipper-like domain. In the C-HR, two tryptophan-rich domains (TRD; pink) are located at the N- and C-terminal regions (N-TRD and C-TRD, respectively). The N-TRD binds to the hydrophobic pocket in the N-HR, whereas the C-TRD plays a key role in membrane association. FP; fusion peptide domain, which penetrates into the target cell membrane. TM; transmembrane region. The amino acid sequence of the HXB2 clone is shown as a representative HIV-1 sequence. Only mutations located in the extracellular domain of gp41 are shown. Mutations observed in in vitro and in vivo selections are indicated by an asterisk (*). I37T was only selected in vitro. Primary and secondary mutations were most frequently associated with T-20 resistance (red and blue, respectively). In addition, T25S/A, S35A/T, R46K, L55F, Q56R/K, V72L, A101I/T/V/G, L108Q, N109D, D113G/N, E119Q, L130V, I135L, N140I, and L158W were selected in patients under T-20 containing regimens, but observed in some drug-naïve HIV-1 strains (Los Alamos HIV Sequence Data Bank, http://www.hiv.lanl.gov/content/index (natural polymorphisms). Corresponding regions of T-20, SC34EK, and T2635 are shown. T-20 is comprised of the original sequence but others are extensively modified. |