Research Article Open Access
About the Evaluation of Liver Disease by the Monitoring of Mahalanobis Distance: Examination for Acute Hepatic Failure
Hisato Nakajima1* Kouya Yano2 Ichirou Takagi31Department of Medical Insurance Guidance Room, The Jikei University Hospital, Japan
2Department of Industrial Engineering and Management, College of Industrial Technology, Nihon University, Japan
3Department of Gastroentero logy and Hepatology, The Jikei University School of Medicine, Japan
- Corresponding Author:
- Hisato Nakajima
Department of Medical Insurance Guidance Room
The Jikei University Hospital, Japan
E-mail: drhisato@icloud.com
Received Date: May 18, 2013; Accepted Date: June 21, 2013; Published Date: June 24, 2013
Citation: Nakajima H, Yano K, Uetake S, Takagi I (2013) About the Evaluation of Liver Disease by the Monitoring of Mahalanobis Distance: Examination for Acute Hepatic Failure. J Community Med Health Educ 3:220. doi: 10.4172/2165-7904.1000220
Copyright: © 2013 Nakajima H, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Visit for more related articles at Journal of Community Medicine & Health Education
Abstract
It is Mahalanobis-Taguchi (MT) system to give the standard to evaluate a process of diagnosis of the doctor commonly. When Mahalanobis distance (MD) is calculated using MT system, it can be grasped as a unitary statistic. MD was calculated using data of fulminant hepatitis and acute on chronic hepatic failure, and a change of MD was compared with the outcome of patients. As a result, it was expressed for the numerical unified value that the data which changed complicatedly. When MD increase, the condition of a patient turns worse. When MD decreases, the condition of a patient is improved. This judgment was enabled easily and was useful as information in the medical treatment.
Keywords
Mahalanobis distance; Mahalanobis-taguchi system; Acute hepatic failure
Introduction
It may be said that the process of thinking that a doctor unifies majority items such as physical views, clinical examination, image diagnosis, and medical care is pattern recognition. It is Mahalanobis- Taguchi (MT) system [1] to give the standard to evaluate that is common to this pattern recognition. Kanetaka [2] used MT system for the judgment of medical examination for the first time. We also reported judgment and cost reduction [3-5] of the medical examination, future prediction of the health condition [6], pathologic grasp and diagnosis of liver disease [7,8]. Particularly, we pointed out that it was the index of liver transplant when a value of Mahalanobis distance (MD) by MT system continued over 1,000 for hepatic failure or hepatocellular carcinoma [9]. Furthermore, for autoimmune liver disease, we reported that the diagnosis of border line of autoimmune liver disease was possible by the reversion of the pattern of figure of factor effect made in MT system [10].
When this MT system is used, and MD is calculated by clinical data, the grasp as the unitary statistic of clinical data becomes possible [8-10]. We calculated MD using clinical data of fulminant hepatitis and acute on chronic hepatic failure this time, and we compared the change of value of MD with the outcome of patient. It was expressed for the numerical unified value that clinical data to change complicatedly. And a pathologic evaluation and a judgment of the curative effect were enabled easily. Because such system was useful as information in the medical treatment, we report it.
Methods
Nineteen acute hepatic failure used for this examination was 15 fulminant hepatitises and four acute on chronic hepatic failure. The details of 19 cases were shown in Table 1. The survivors were four fulminant hepatitises and were one acute type, three subacute type. The death was 15 cases and was three fulminant hepatitises acute type, eight subacute type and four acute on chronic hepatic failure.
| Case | Sex | Age | Diagnosis and type | Cause | Prognosis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Male | 24 | Fluminant hepatitius | acute | HBV | alive | |
| 2 | Female | 22 | Fluminant hepatitius | subacute | HBV | alive | |
| 3 | Male | 50 | Fluminant hepatitius | subacute | drug | alive | |
| 4 | Male | 51 | Fluminant hepatitius | subacute | unknown | alive | |
| 5 | Male | 48 | Fluminant hepatitius | acute | HBV | dead | renal failure |
| 6 | Male | 54 | Fluminant hepatitius | acute | unknown | dead | hepatic failure |
| 7 | Female | 45 | Fluminant hepatitius | acute | unknown | dead | hepatic failure |
| 8 | Male | 32 | Fluminant hepatitius | subacute | HBV | dead | hepatic failure |
| 9 | Male | 73 | Fluminant hepatitius | subacute | HBV | dead | hepatic failure |
| 10 | Male | 73 | Fluminant hepatitius | subacute | HBV | dead | renal failure |
| 11 | Male | 28 | Fluminant hepatitius | subacute | HBV | dead | GI bleeding |
| 12 | Female | 71 | Fluminant hepatitius | subacute | drug | dead | hepatic failure |
| 13 | Male | 34 | Fluminant hepatitius | subacute | unknown | dead | hepatic failure |
| 14 | Male | 40 | Fluminant hepatitius | subacute | unknown | dead | hepatic failure |
| 15 | Male | 57 | Fluminant hepatitius | subacute | unknown | dead | GI bleeding |
| 16 | Male | 50 | Acute on chronic | Budd Chiari | dead | renal failure | |
| 17 | Male | 51 | Acute on chronic | cirrhosis | dead | GI bleeding | |
| 18 | Female | 71 | Acute on chronic | HBV | dead | renal failure | |
| 19 | Female | 62 | Acute on chronic | alcohol | dead | renal failure | |
Table 1: The details of 15 cases of fluminant hepatitis and 4 cases of acuto on chronic.
The data of following 18 items were used for this examination. There was the item in hepatic coma grade (coma), ammonia (NH3) microgram/dl, number of platelets (PLT) 109/L, prothrombin time (PT) %, hepaplastin test (HPT)%, aspartate aminotransferase (AST)/ IU/L, alanine aminotransferase (ALT) IU/L, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) IU/L, cholinesterase (ChE) IU/L, total bilirubin (T.B) mg/dl, alkaline phosphatase (ALP) IU/L, leucineaminopeptidase (LAP) IU/L, gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase (rGT) IU/L, Urea nitrogen(UN) mg/ dL, creatinine (Cr) mg/dL, total cholesterol (T.C) mg/dL, total protein (T.P) g/dL, albumin (ALB) g/dL.
The unit space of MT system is defined individually. In addition, it is evaluated how much an object is away from the unit space by a level of MD. MT system is divided into MT method, MT Ajoint method, Taguchi-Schmidt method and Taguchi method. The MT method used this time is a method using an inverse matrix using MD, and it’s precision is higher than other methods. It is the characteristic of this method that the target average by unit space becomes “MD=1”. The data of 18 items of 30 physically normal people were shown in Table 2, and these data were used for making of the unit space. In addition, the data of each case used for examination were shown in Tables 3-5. The data of 18 items of these 19 cases were used, and MD was calculated by MT method. Hepatic coma grade assumed it a five level from zero, and numerical value data were just used for other 17 items.
| coma | NH3 | PLT | PT | HPT | AST | ALT | LDH | ChE | T.B. | ALP | LAP | rGT | UN | Cr | T.C. | T.P. | Alb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 38 | 20.4 | 97 | 74 | 14 | 6 | 219 | 580 | 0.2 | 299 | 187 | 18 | 9 | 0.6 | 187 | 6.7 | 3.8 |
| 0 | 35 | 33.3 | 87 | 88 | 17 | 21 | 217 | 334 | 0.6 | 332 | 225 | 44 | 19 | 0.4 | 200 | 6.9 | 4.1 |
| 0 | 29 | 24.9 | 87 | 100 | 12 | 10 | 216 | 385 | 0.4 | 306 | 195 | 17 | 15 | 0.5 | 198 | 6.7 | 3.5 |
| 0 | 21 | 24.8 | 93 | 100 | 23 | 26 | 206 | 598 | 0.5 | 287 | 210 | 25 | 8 | 1 | 214 | 8.2 | 4.3 |
| 0 | 35 | 20.5 | 100 | 94 | 19 | 15 | 215 | 378 | 0.4 | 386 | 207 | 26 | 14 | 0.9 | 202 | 7.1 | 3.7 |
| 0 | 24 | 31.2 | 94 | 96 | 28 | 21 | 226 | 505 | 0.7 | 312 | 227 | 23 | 9 | 0.3 | 216 | 6.7 | 3.9 |
| 0 | 39 | 25.4 | 70 | 90 | 17 | 13 | 226 | 361 | 0.7 | 178 | 186 | 10 | 14 | 0.4 | 149 | 6.8 | 4.1 |
| 0 | 20 | 22.8 | 84 | 81 | 16 | 14 | 223 | 427 | 0.4 | 261 | 240 | 48 | 15 | 0.6 | 208 | 7.1 | 4.1 |
| 0 | 40 | 26.1 | 100 | 100 | 13 | 12 | 205 | 568 | 0.3 | 300 | 267 | 8 | 10 | 0.8 | 213 | 7.8 | 4.7 |
| 0 | 31 | 22.1 | 89 | 93 | 12 | 14 | 144 | 336 | 0.8 | 136 | 143 | 38 | 17 | 0.7 | 147 | 6.9 | 4.5 |
| 0 | 39 | 27.4 | 87 | 81 | 11 | 9 | 145 | 280 | 0.2 | 140 | 137 | 2 | 18 | 0.8 | 139 | 6.9 | 3.9 |
| 0 | 29 | 20.9 | 97 | 100 | 18 | 16 | 194 | 623 | 0.8 | 201 | 208 | 23 | 15 | 0.7 | 183 | 7.2 | 4.1 |
| 0 | 38 | 24.4 | 100 | 100 | 24 | 23 | 242 | 556 | 0.8 | 194 | 182 | 10 | 17 | 0.4 | 218 | 7.2 | 4.4 |
| 0 | 47 | 29.1 | 94 | 94 | 21 | 21 | 176 | 700 | 0.4 | 267 | 161 | 11 | 18 | 0.5 | 189 | 6.8 | 4.2 |
| 0 | 20 | 28.4 | 86 | 93 | 13 | 11 | 199 | 486 | 0.5 | 400 | 229 | 8 | 14 | 0.6 | 133 | 7.1 | 4.1 |
| 0 | 38 | 31.3 | 87 | 100 | 10 | 6 | 170 | 614 | 0.2 | 315 | 169 | 13 | 11 | 0.3 | 199 | 7.2 | 4.1 |
| 0 | 47 | 33.6 | 93 | 93 | 12 | 12 | 236 | 518 | 1.1 | 246 | 179 | 19 | 19 | 0.4 | 193 | 7.2 | 4.4 |
| 0 | 44 | 18.2 | 81 | 100 | 21 | 19 | 240 | 700 | 0.5 | 204 | 202 | 17 | 17 | 0.5 | 195 | 7.9 | 4.4 |
| 0 | 36 | 33.6 | 90 | 100 | 12 | 22 | 169 | 433 | 0.7 | 305 | 171 | 28 | 18 | 0.8 | 160 | 7.2 | 4.2 |
| 0 | 50 | 21.2 | 87 | 100 | 13 | 17 | 194 | 671 | 0.6 | 273 | 204 | 41 | 8 | 0.6 | 200 | 7.5 | 4.4 |
| 0 | 34 | 30.9 | 96 | 100 | 10 | 4 | 230 | 546 | 0.8 | 346 | 213 | 41 | 16 | 1 | 213 | 6.7 | 4.2 |
| 0 | 21 | 35.5 | 100 | 100 | 18 | 21 | 210 | 658 | 0.5 | 171 | 194 | 17 | 12 | 0.9 | 193 | 7.8 | 5.1 |
| 0 | 27 | 18.9 | 96 | 100 | 27 | 27 | 205 | 483 | 1.1 | 336 | 189 | 51 | 11 | 0.8 | 174 | 7.1 | 4.2 |
| 0 | 32 | 19.6 | 86 | 84 | 15 | 17 | 182 | 524 | 0.7 | 258 | 165 | 4 | 12 | 0.7 | 138 | 7.1 | 4.2 |
| 0 | 45 | 19.3 | 100 | 100 | 12 | 9 | 183 | 593 | 0.7 | 192 | 155 | 13 | 11 | 0.8 | 202 | 7.1 | 4.2 |
| 0 | 26 | 17.9 | 100 | 95 | 17 | 14 | 224 | 644 | 0.4 | 252 | 178 | 34 | 20 | 0.6 | 202 | 6.9 | 4.5 |
| 0 | 45 | 25.7 | 90 | 90 | 16 | 17 | 237 | 463 | 0.6 | 162 | 225 | 21 | 17 | 0.5 | 216 | 7.4 | 4.3 |
| 0 | 26 | 27.3 | 89 | 100 | 21 | 19 | 196 | 549 | 8 | 221 | 170 | 26 | 16 | 0.7 | 213 | 7.7 | 5.1 |
| 0 | 41 | 31.7 | 97 | 100 | 6 | 2 | 141 | 314 | 0.3 | 185 | 172 | 5 | 14 | 0.8 | 141 | 7.1 | 3.8 |
| 0 | 30 | 28.1 | 100 | 100 | 14 | 7 | 215 | 290 | 0.7 | 214 | 158 | 6 | 10 | 0.7 | 175 | 7.5 | 3.7 |
Table 2: The data of 18 items of 30 physically normal people who underwent a medical examination.
| coma | NH3 | PLT | PT | HPT | AST | ALT | LDH | ChE | T.B. | ALP | LAP | rGT | UN | Cr | T.C. | T.P. | Alb |
| 1 | 8 | 6.4 | 23 | 13 | 1292 | 3004 | 509 | 243 | 8.7 | 639 | 408 | 46 | 12 | 1.1 | 70 | 5.8 | 3.6 |
| 1 | 84 | 8.6 | 36 | 20 | 400 | 1770 | 270 | 258 | 8.2 | 623 | 284 | 47 | 9 | 1 | 68 | 6 | 3.3 |
| 1 | 92 | 9.4 | 62 | 23 | 194 | 1393 | 239 | 312 | 8 | 623 | 3.6 | 47 | 10 | 1 | 99 | 7 | 3.9 |
| 2 | 54 | 9.9 | 84 | 61 | 89 | 429 | 235 | 400 | 5.7 | 479 | 236 | 36 | 11 | 0.8 | 120 | 6.1 | 3.8 |
| 3 | 82 | 13.4 | 96 | 80 | 60 | 388 | 218 | 443 | 7.1 | 479 | 275 | 57 | 12 | 1 | 120 | 7.4 | 3.9 |
| 2 | 36 | 17.6 | 97 | 83 | 46 | 323 | 220 | 474 | 5.4 | 479 | 294 | 88 | 11 | 1 | 128 | 7.1 | 4.3 |
| 1 | 36 | 18.6 | 100 | 93 | 37 | 205 | 200 | 450 | 5.2 | 463 | 300 | 100 | 12 | 1.1 | 130 | 7 | 4 |
| 0 | 40 | 20.7 | 100 | 93 | 36 | 198 | 197 | 479 | 4.1 | 447 | 320 | 107 | 13 | 0.6 | 125 | 7.1 | 4.3 |
| 0 | 34 | 21.3 | 100 | 93 | 40 | 159 | 236 | 513 | 3.4 | 431 | 320 | 122 | 13 | 0.6 | 130 | 7.1 | 4.3 |
| 0 | 34 | 31.1 | 96 | 88 | 39 | 122 | 207 | 511 | 2.8 | 479 | 345 | 131 | 16 | 0.7 | 128 | 7.1 | 4.3 |
| 0 | 46 | 34 | 97 | 80 | 36 | 104 | 195 | 495 | 2.9 | 431 | 321 | 127 | 12 | 0.8 | 140 | 7 | 4 |
| 0 | 46 | 34.3 | 100 | 102 | 33 | 65 | 146 | 533 | 2.1 | 415 | 316 | 107 | 13 | 0.9 | 153 | 6.7 | 4.1 |
| 0 | 34 | 30.4 | 96 | 100 | 33 | 58 | 197 | 461 | 1.6 | 431 | 325 | 70 | 13 | 0.8 | 150 | 7.1 | 4.5 |
Case 1: acute type
| coma | NH3 | PLT | PT | HPT | AST | ALT | LDH | ChE | T.B. | ALP | LAP | rGT | UN | Cr | T.C. | T.P. | Alb |
| 4 | 150 | 1.2 | 13 | 10 | 290 | 1350 | 1234 | 6.5 | 29.4 | 670 | 322 | 44 | 9.2 | 1.1 | 135 | 7 | 4.2 |
| 4 | 160 | 1.6 | 20 | 10 | 134 | 245 | 955 | 5.3 | 18.4 | 399 | 157 | 11 | 18 | 1.2 | 151 | 6.9 | 4 |
| 4 | 173 | 1.3 | 15 | 10 | 91 | 88 | 652 | 7.3 | 14.2 | 351 | 172 | 22 | 20 | 1.2 | 124 | 6.2 | 3.9 |
| 4 | 140 | 1.6 | 20 | 15 | 100 | 143 | 620 | 7.1 | 15.6 | 335 | 283 | 71 | 29 | 1 | 124 | 6.7 | 3.9 |
| 4 | 150 | 1.2 | 25 | 18 | 120 | 209 | 715 | 7.5 | 19.4 | 447 | 400 | 116 | 23 | 0.9 | 145 | 6.9 | 3.8 |
| 4 | 127 | 1 | 43 | 25 | 122 | 256 | 864 | 7.2 | 22.4 | 463 | 436 | 138 | 23 | 0.9 | 140 | 7.1 | 4.3 |
| 3 | 110 | 1.7 | 50 | 35 | 58 | 121 | 589 | 7.5 | 12.4 | 319 | 296 | 97 | 15.8 | 0.8 | 135 | 7 | 4 |
| 1 | 80 | 1.6 | 55 | 40 | 98 | 246 | 694 | 7.6 | 27 | 590 | 454 | 213 | 18 | 1 | 151 | 7.1 | 4.3 |
| 1 | 75 | 3.1 | 65 | 50 | 90 | 188 | 486 | 6.6 | 17.8 | 638 | 357 | 264 | 25 | 0.8 | 124 | 7 | 4 |
| 0 | 60 | 2.4 | 100 | 80 | 86 | 168 | 389 | 6.5 | 9.6 | 702 | 486 | 349 | 21.4 | 0.9 | 124 | 7.1 | 4.3 |
| 0 | 55 | 1.8 | 90 | 80 | 107 | 236 | 375 | 6 | 7.1 | 862 | 681 | 442 | 18 | 0.7 | 130 | 7.2 | 4.2 |
| 0 | 61 | 1.6 | 80 | 70 | 119 | 252 | 455 | 5 | 8.1 | 926 | 742 | 475 | 19.9 | 0.7 | 140 | 7.1 | 4.3 |
| 0 | 60 | 1.9 | 93 | 85 | 57 | 172 | 460 | 5.2 | 6.4 | 1069 | 822 | 529 | 19 | 0.7 | 135 | 7 | 4 |
| 0 | 60 | 1.8 | 72 | 65 | 39 | 91 | 537 | 7.1 | 6.1 | 1117 | 868 | 554 | 19.5 | 0.6 | 151 | 7.1 | 4.3 |
| 0 | 78 | 2.2 | 70 | 65 | 36 | 68 | 466 | 6.9 | 4.1 | 1054 | 747 | 527 | 18 | 0.7 | 124 | 7.2 | 4.2 |
Case 2: subacute type
| coma | NH3 | PLT | PT | HPT | AST | ALT | LDH | ChE | T.B. | ALP | LAP | rGT | UN | Cr | T.C. | T.P. | Alb |
| 2 | 94 | 13.6 | 44 | 29 | 374 | 605 | 333 | 259 | 20.4 | 702 | 484 | 257 | 14 | 1.3 | 130 | 6.2 | 3 |
| 2 | 80 | 15.5 | 40 | 27 | 232 | 433 | 288 | 263 | 23.3 | 718 | 489 | 263 | 10 | 1.1 | 131 | 6.5 | 3 |
| 2 | 100 | 15.6 | 44 | 27 | 168 | 348 | 262 | 253 | 23.8 | 750 | 455 | 229 | 16 | 1.4 | 120 | 6.3 | 3 |
| 2 | 82 | 18 | 49 | 28 | 118 | 268 | 239 | 254 | 21.6 | 654 | 459 | 209 | 18 | 1 | 117 | 6 | 2.8 |
| 2 | 102 | 12.7 | 46 | 33 | 83 | 197 | 269 | 318 | 23.6 | 702 | 476 | 175 | 17 | 1 | 135 | 6.8 | 3.3 |
| 1 | 60 | 16.5 | 47 | 31 | 58 | 88 | 231 | 350 | 12 | 622 | 619 | 120 | 18 | 1 | 160 | 6 | 3.1 |
| 1 | 80 | 11.1 | 46 | 30 | 64 | 78 | 280 | 301 | 8.1 | 574 | 367 | 122 | 16 | 1.1 | 141 | 5.8 | 2.9 |
| 0 | 70 | 11 | 53 | 30 | 50 | 52 | 211 | 269 | 8.2 | 686 | 375 | 140 | 23 | 1 | 139 | 5.8 | 2.9 |
| 0 | 74 | 6.5 | 58 | 35 | 43 | 41 | 194 | 255 | 7 | 622 | 345 | 125 | 25 | 1 | 140 | 5.8 | 2.6 |
| 0 | 80 | 8.5 | 72 | 45 | 45 | 37 | 253 | 223 | 3.7 | 782 | 366 | 94 | 16 | 1 | 129 | 5.4 | 2.5 |
Case 3: subacute type
| coma | NH3 | PLT | PT | HPT | AST | ALT | LDH | ChE | T.B. | ALP | LAP | rGT | UN | Cr | T.C. | T.P. | Alb |
| 2 | 150 | 8 | 30 | 20 | 670 | 845 | 242 | 179 | 0.3 | 559 | 237 | 171 | 48 | 1.1 | 63 | 6.4 | 2.9 |
| 2 | 87 | 6.6 | 35 | 29 | 255 | 391 | 306 | 148 | 23.2 | 512 | 193 | 148 | 37 | 0.7 | 59 | 5.7 | 2.3 |
| 2 | 80 | 5.7 | 35 | 28 | 212 | 233 | 286 | 143 | 26.2 | 522 | 162 | 106 | 28 | 0.7 | 56 | 5.9 | 2.2 |
| 1 | 62 | 5.5 | 35 | 30 | 159 | 144 | 244 | 110 | 28.9 | 506 | 142 | 61 | 44 | 1.3 | 56 | 5.7 | 2.1 |
| 0 | 39 | 3.3 | 40 | 34 | 108 | 72 | 224 | 143 | 26.6 | 461 | 156 | 52 | 43 | 1.5 | 60 | 6 | 2.6 |
| 0 | 40 | 1.5 | 35 | 32 | 99 | 56 | 230 | 148 | 27.9 | 500 | 170 | 60 | 45 | 1.4 | 69 | 6 | 2.5 |
| 0 | 50 | 3.4 | 40 | 35 | 92 | 50 | 200 | 201 | 22.2 | 450 | 160 | 50 | 39 | 1.3 | 80 | 6.3 | 2.7 |
| 0 | 55 | 7.7 | 45 | 40 | 73 | 40 | 210 | 254 | 22.4 | 460 | 170 | 50 | 45 | 1.5 | 95 | 6.3 | 2.8 |
| 0 | 60 | 10.6 | 40 | 29 | 63 | 33 | 196 | 380 | 26 | 398 | 152 | 37 | 40 | 1.3 | 146 | 7.3 | 3.1 |
| 0 | 60 | 10.5 | 55 | 50 | 36 | 19 | 203 | 349 | 13.7 | 256 | 150 | 23 | 45 | 1.4 | 121 | 6 | 3.4 |
| 0 | 62 | 11.8 | 75 | 70 | 68 | 31 | 169 | 370 | 13.5 | 315 | 193 | 41 | 40 | 1.4 | 120 | 6.9 | 3.5 |
| 0 | 55 | 15.4 | 60 | 52 | 59 | 27 | 183 | 349 | 10.2 | 334 | 201 | 45 | 35 | 1.3 | 110 | 7.6 | 3.6 |
| 0 | 50 | 13.5 | 80 | 74 | 141 | 53 | 206 | 444 | 9.6 | 449 | 276 | 86 | 45 | 1.2 | 162 | 6.8 | 4.7 |
| 0 | 50 | 14.2 | 90 | 86 | 144 | 62 | 201 | 491 | 9.5 | 471 | 322 | 80 | 58 | 1.6 | 202 | 9.5 | 4.6 |
| 0 | 45 | 10 | 65 | 50 | 89 | 47 | 167 | 333 | 10 | 390 | 257 | 76 | 23 | 1 | 154 | 7.9 | 3.5 |
| 0 | 40 | 27.3 | 75 | 62 | 50 | 24 | 169 | 233 | 6.1 | 299 | 230 | 63 | 12 | 0.9 | 140 | 7.3 | 3.2 |
| 0 | 45 | 24.5 | 70 | 60 | 45 | 20 | 156 | 190 | 4.5 | 260 | 205 | 58 | 11 | 0.9 | 137 | 6.4 | 2.8 |
| 0 | 50 | 11.8 | 70 | 62 | 40 | 16 | 136 | 190 | 2.8 | 271 | 219 | 65 | 14 | 1 | 176 | 6.7 | 2.9 |
| 0 | 41 | 12.3 | 75 | 65 | 37 | 19 | 149 | 201 | 1.8 | 301 | 243 | 74 | 14 | 1 | 204 | 7.5 | 3.3 |
Case 4: subacute type
Table 3: The data of 4 survival cases of fluminant hepatitis used for examination.
| coma | NH3 | PLT | PT | HPT | AST | ALT | LDH | ChE | T.B. | ALP | LAP | rGT | UN | Cr | T.C. | T.P. | Alb |
| 2 | 140 | 9.3 | 10 | 10 | 7611 | 4665 | 7006 | 431 | 5.6 | 1070 | 1133 | 108 | 25 | 1.2 | 75 | 6.7 | 3.6 |
| 3 | 152 | 5.2 | 10 | 10 | 5470 | 3060 | 5620 | 368 | 6.9 | 894 | 525 | 81 | 19 | 2.1 | 61 | 5.3 | 3.7 |
| 3 | 146 | 5.5 | 10 | 10 | 3249 | 2620 | 1844 | 228 | 8.2 | 639 | 638 | 56 | 17 | 2.8 | 57 | 5.5 | 3.1 |
| 5 | 508 | 6.8 | 10 | 10 | 1000 | 1330 | 632 | 198 | 10.5 | 575 | 415 | 41 | 14 | 4.8 | 116 | 5.3 | 3.3 |
| 5 | 214 | 8 | 17 | 18 | 325 | 281 | 1404 | 288 | 7 | 149 | 245 | 18 | 12 | 7.7 | 88 | 4.7 | 2.6 |
Case 5: acute type
| coma | NH3 | PLT | PT | HPT | AST | ALT | LDH | ChE | T.B. | ALP | LAP | rGT | UN | Cr | T.C. | T.P. | Alb |
| 2 | 117 | 13.5 | 18 | 10 | 296 | 247 | 400 | 107 | 17.3 | 471 | 304 | 28 | 5 | 0.4 | 87 | 5.4 | 2.5 |
| 2 | 138 | 13.2 | 22 | 12 | 197 | 182 | 354 | 175 | 15.1 | 412 | 275 | 26 | 16 | 0.8 | 89 | 5 | 2.2 |
| 3 | 107 | 8.3 | 24 | 17 | 44 | 54 | 306 | 474 | 12.3 | 303 | 182 | 23 | 14 | 0.5 | 187 | 5.4 | 3 |
| 3 | 180 | 8.6 | 24 | 14 | 45 | 50 | 325 | 437 | 11.3 | 255 | 169 | 18 | 10 | 0.6 | 155 | 5.3 | 3 |
| 4 | 138 | 8.2 | 23 | 16 | 184 | 128 | 417 | 472 | 10.2 | 245 | 163 | 21 | 16 | 0.8 | 153 | 5.1 | 2.7 |
| 5 | 107 | 5.7 | 22 | 15 | 274 | 196 | 547 | 481 | 10.9 | 258 | 182 | 29 | 14 | 0.5 | 161 | 5.3 | 3 |
| 5 | 180 | 6.5 | 24 | 14 | 256 | 184 | 540 | 438 | 11.4 | 287 | 215 | 32 | 10 | 0.6 | 169 | 5.8 | 2.3 |
Case 6: acute type
| coma | NH3 | PLT | PT | HPT | AST | ALT | LDH | ChE | T.B. | ALP | LAP | rGT | UN | Cr | T.C. | T.P. | Alb |
| 2 | 100 | 28.1 | 10 | 10 | 1440 | 1455 | 1748 | 274 | 10 | 814 | 267 | 43 | 25 | 0.5 | 103 | 5.9 | 3 |
| 2 | 110 | 15.7 | 12 | 5 | 299 | 341 | 516 | 374 | 5.7 | 415 | 157 | 21 | 30 | 0.7 | 110 | 5.8 | 3.1 |
| 4 | 201 | 13 | 14 | 4 | 226 | 240 | 349 | 342 | 9.3 | 463 | 184 | 17 | 27 | 0.6 | 140 | 5.8 | 2.9 |
| 4 | 209 | 5 | 10 | 6 | 160 | 250 | 451 | 360 | 9.2 | 463 | 190 | 16 | 28 | 0.6 | 150 | 5.7 | 3 |
| 4 | 133 | 6 | 10 | 4 | 64 | 116 | 448 | 432 | 12.8 | 447 | 449 | 250 | 32 | 0.7 | 140 | 5.5 | 2.8 |
| 4 | 150 | 7 | 12 | 5 | 31 | 41 | 400 | 456 | 8 | 527 | 170 | 502 | 31 | 0.7 | 130 | 5.6 | 2.8 |
| 5 | 210 | 5 | 14 | 10 | 43 | 55 | 398 | 420 | 13.2 | 511 | 210 | 676 | 29 | 0.6 | 140 | 5.4 | 2.7 |
| 5 | 230 | 6 | 10 | 10 | 231 | 96 | 420 | 498 | 11.2 | 571 | 190 | 1638 | 35 | 0.8 | 135 | 5.5 | 2.6 |
Case 7: acute type
| coma | NH3 | PLT | PT | HPT | AST | ALT | LDH | ChE | T.B. | ALP | LAP | rGT | UN | Cr | T.C. | T.P. | Alb |
| 2 | 170 | 22.1 | 19.9 | 10 | 342 | 353 | 533 | 158 | 35.2 | 2603 | 431 | 22 | 8 | 1.2 | 89 | 5.1 | 3.3 |
| 2 | 185 | 16.7 | 44.1 | 30 | 277 | 177 | 676 | 155 | 26.4 | 1517 | 299 | 12 | 9 | 1.1 | 107 | 5.5 | 3.6 |
| 3 | 148 | 16.1 | 54.2 | 45 | 343 | 210 | 699 | 160 | 26 | 1781 | 265 | 8 | 9 | 1 | 149 | 6.7 | 4.2 |
| 5 | 120 | 18.4 | 34.4 | 30 | 382 | 217 | 699 | 145 | 25.5 | 1533 | 261 | 9 | 23 | 1.8 | 132 | 5.9 | 3.3 |
| 5 | 150 | 8.9 | 44.1 | 35 | 129 | 254 | 844 | 150 | 18.9 | 1628 | 252 | 4 | 33 | 2.1 | 181 | 6.3 | 3.8 |
| 5 | 43 | 6.5 | 24 | 15 | 210 | 99 | 580 | 120 | 23.2 | 1837 | 286 | 11 | 51 | 3.5 | 137 | 5.6 | 3.5 |
| 5 | 85 | 6.9 | 28.3 | 25 | 437 | 165 | 1478 | 135 | 19.6 | 1438 | 256 | 6 | 49 | 2.5 | 135 | 5.6 | 3.5 |
| 5 | 63 | 6.6 | 26.7 | 25 | 284 | 312 | 1725 | 145 | 22.2 | 1724 | 284 | 11 | 43 | 1.9 | 176 | 5.6 | 3.3 |
| 5 | 57 | 4.7 | 24 | 20 | 144 | 209 | 2024 | 130 | 26.8 | 2178 | 327 | 14 | 55 | 2.4 | 193 | 6.2 | 3.7 |
Case 8: subacute type
| coma | NH3 | PLT | PT | HPT | AST | ALT | LDH | ChE | T.B. | ALP | LAP | rGT | UN | Cr | T.C. | T.P. | Alb |
| 2 | 40 | 18.2 | 40 | 33 | 183 | 197 | 346 | 190 | 23.3 | 527 | 283 | 47 | 32 | 1.7 | 72 | 5.6 | 2.5 |
| 2 | 38 | 21.3 | 46 | 46 | 140 | 142 | 332 | 266 | 26.5 | 606 | 296 | 47 | 17 | 1.7 | 84 | 6 | 2.7 |
| 1 | 36 | 17.2 | 38 | 37 | 131 | 134 | 322 | 272 | 27.2 | 590 | 281 | 46 | 14 | 1.5 | 83 | 5.9 | 2.7 |
| 2 | 36 | 16.8 | 39 | 32 | 110 | 98 | 301 | 277 | 27.6 | 606 | 281 | 44 | 11 | 1.4 | 85 | 5.8 | 2.5 |
| 2 | 36 | 17.5 | 45 | 37 | 123 | 112 | 365 | 326 | 35 | 782 | 326 | 52 | 11 | 1.3 | 95 | 6.7 | 3 |
| 2 | 28 | 11.2 | 72 | 67 | 63 | 48 | 250 | 384 | 23 | 415 | 218 | 30 | 9 | 1.6 | 113 | 5.6 | 3 |
| 2 | 28 | 13 | 51 | 65 | 72 | 51 | 279 | 393 | 24.5 | 511 | 248 | 37 | 9 | 1.5 | 128 | 6.3 | 3.3 |
| 1 | 18 | 12.7 | 41 | 52 | 66 | 48 | 250 | 394 | 24.7 | 590 | 269 | 42 | 10 | 1.5 | 116 | 6.4 | 3.3 |
| 1 | 24 | 8.9 | 34 | 39 | 43 | 27 | 207 | 328 | 17.7 | 367 | 168 | 25 | 9 | 1.6 | 102 | 5.3 | 3 |
| 2 | 28 | 10.3 | 41 | 57 | 44 | 29 | 228 | 326 | 19.4 | 415 | 208 | 30 | 9 | 1.4 | 106 | 5.5 | 3 |
| 2 | 30 | 11.7 | 38 | 54 | 46 | 27 | 241 | 360 | 19.7 | 479 | 238 | 37 | 8 | 1.4 | 116 | 5.6 | 3.1 |
| 2 | 40 | 9.7 | 52 | 67 | 34 | 19 | 219 | 375 | 16.2 | 351 | 184 | 32 | 7 | 1.4 | 128 | 5.5 | 3.2 |
| 2 | 36 | 10.1 | 41 | 40 | 35 | 21 | 246 | 407 | 19 | 447 | 226 | 38 | 8 | 1.4 | 142 | 6.1 | 3.3 |
| 2 | 40 | 10.4 | 32 | 29 | 31 | 19 | 260 | 411 | 22.4 | 479 | 267 | 43 | 8 | 1.4 | 136 | 6.2 | 3.3 |
| 2 | 40 | 9.9 | 37 | 42 | 47 | 19 | 315 | 423 | 22.8 | 588 | 267 | 40 | 11 | 1.3 | 126 | 6.5 | 3.5 |
| 1 | 44 | 8.2 | 48 | 37 | 26 | 13 | 248 | 372 | 19.4 | 415 | 199 | 30 | 12 | 1.3 | 145 | 5.9 | 3.3 |
| 1 | 28 | 7.1 | 38 | 31 | 30 | 11 | 287 | 377 | 21.6 | 479 | 220 | 42 | 9 | 1.4 | 129 | 6 | 3.2 |
| 1 | 42 | 6.8 | 42 | 29 | 31 | 15 | 307 | 397 | 23 | 511 | 237 | 40 | 13 | 1.1 | 131 | 6.2 | 3.4 |
| 2 | 32 | 7.8 | 42 | 50 | 30 | 12 | 307 | 397 | 23 | 511 | 251 | 52 | 22 | 1.2 | 126 | 6.6 | 3.5 |
| 2 | 42 | 9.3 | 32 | 40 | 33 | 13 | 319 | 432 | 23.5 | 542 | 294 | 71 | 29 | 1.3 | 111 | 7.3 | 3.6 |
| 2 | 56 | 10.7 | 37 | 29 | 28 | 9 | 284 | 403 | 22.3 | 558 | 276 | 72 | 30 | 1.4 | 103 | 6.9 | 3.6 |
| 2 | 48 | 10.8 | 48 | 42 | 21 | 10 | 291 | 430 | 19.8 | 479 | 249 | 47 | 33 | 1.2 | 120 | 7.1 | 4 |
| 2 | 52 | 12.4 | 38 | 37 | 21 | 5 | 278 | 434 | 20.8 | 542 | 267 | 59 | 33 | 1.2 | 116 | 6.8 | 3.9 |
| 2 | 70 | 12.1 | 42 | 31 | 21 | 7 | 276 | 450 | 23.6 | 606 | 274 | 54 | 29 | 1.2 | 111 | 7.4 | 3.7 |
| 2 | 48 | 14.7 | 42 | 29 | 60 | 13 | 953 | 369 | 28 | 702 | 316 | 51 | 44 | 1.9 | 62 | 7.1 | 3.5 |
| 3 | 68 | 18.5 | 20 | 30 | 58 | 13 | 507 | 326 | 15.9 | 383 | 193 | 25 | 41 | 1.8 | 97 | 5.7 | 3.1 |
Case 9: subacute type
| coma | NH3 | PLT | PT | HPT | AST | ALT | LDH | ChE | T.B. | ALP | LAP | rGT | UN | Cr | T.C. | T.P. | Alb |
| 1 | 126 | 8.3 | 10 | 10 | 3611 | 2596 | 4338 | 406 | 9 | 782 | 516 | 117 | 28 | 1.6 | 145 | 6.2 | 2.7 |
| 1 | 70 | 8.4 | 17 | 11.5 | 3061 | 2040 | 4846 | 444 | 11 | 766 | 511 | 101 | 26 | 1.7 | 145 | 7 | 4.1 |
| 3 | 64 | 6.4 | 15 | 12 | 845 | 665 | 1960 | 460 | 8.6 | 782 | 490 | 352 | 16 | 2.1 | 160 | 5.3 | 3 |
| 4 | 122 | 6.3 | 10 | 10 | 644 | 746 | 1599 | 422 | 14.3 | 574 | 277 | 45 | 10 | 1.6 | 181 | 5.9 | 3.1 |
| 5 | 122 | 7.3 | 14 | 19.5 | 109 | 172 | 759 | 357 | 12.7 | 351 | 179 | 20 | 10 | 1.8 | 156 | 5.5 | 3.1 |
| 5 | 160 | 9.6 | 21 | 33 | 81 | 73 | 803 | 368 | 11.4 | 351 | 164 | 17 | 9 | 2.9 | 148 | 6.7 | 3.7 |
Case 10: subacute type
| coma | NH3 | PLT | PT | HPT | AST | ALT | LDH | ChE | T.B. | ALP | LAP | rGT | UN | Cr | T.C. | T.P. | Alb |
| 2 | 136 | 11.6 | 22.5 | 19.8 | 126 | 141 | 476 | 3.5 | 22.6 | 590 | 323 | 51 | 8 | 0.8 | 88 | 5 | 2.5 |
| 2 | 145 | 5 | 17 | 10 | 135 | 133 | 483 | 2.7 | 21 | 590 | 301 | 42 | 7.6 | 0.8 | 73 | 3.9 | 2 |
| 2 | 157 | 4.7 | 31 | 21.5 | 80 | 80 | 435 | 4.6 | 17.8 | 399 | 213 | 43 | 8 | 1 | 89 | 4.6 | 2.8 |
| 1 | 185 | 5 | 34 | 26 | 115 | 107 | 369 | 4.1 | 15.4 | 351 | 170 | 45 | 8.9 | 0.9 | 110 | 5 | 3.2 |
| 2 | 208 | 4.2 | 35 | 29 | 50 | 51 | 346 | 8.3 | 10.4 | 335 | 190 | 40 | 10.7 | 0.7 | 153 | 5.2 | 3.5 |
| 3 | 211 | 4.6 | 25 | 21 | 52 | 58 | 364 | 8.3 | 10.8 | 351 | 205 | 43 | 13.4 | 0.8 | 130 | 5.3 | 3.4 |
| 3 | 256 | 6 | 23 | 13 | 54 | 72 | 383 | 7.9 | 12.3 | 383 | 213 | 45 | 15 | 0.7 | 175 | 5.6 | 3.5 |
| 3 | 199 | 7.2 | 22.5 | 21 | 63 | 79 | 390 | 8.7 | 14.4 | 383 | 170 | 55 | 12.2 | 0.7 | 154 | 5.3 | 2.9 |
| 4 | 157 | 8.8 | 22 | 11.5 | 79 | 94 | 467 | 9 | 15.8 | 415 | 250 | 70 | 13.8 | 0.6 | 145 | 5.2 | 3 |
| 3 | 228 | 21 | 20.5 | 67 | 86 | 445 | 8.7 | 16.4 | 367 | 358 | 95 | 15 | 0.7 | 140 | 5 | 3.1 | |
| 5 | 238 | 10.2 | 23 | 26.5 | 56 | 64 | 480 | 8.5 | 13.1 | 271 | 221 | 42 | 12.7 | 0.6 | 134 | 4.9 | 2.8 |
Case 11: subacute type
Table 4: The data of 7 dead cases of fluminant hepatitis used for examination.
| Coma | NH3 | PLT | PT | HPT | AST | ALT | LDH | ChE | T.B. | ALP | LAP | rGT | UN | Cr | T.C. | T.P. | Alb |
| 2 | 70 | 6 | 61 | 40 | 742 | 537 | 652 | 177 | 13.9 | 443 | 387 | 65 | 5 | 0.4 | 109 | 5.5 | 2.8 |
| 3 | 90 | 6.5 | 46 | 31 | 647 | 540 | 644 | 167 | 18.7 | 391 | 375 | 63 | 16 | 0.8 | 117 | 5.4 | 2.9 |
| 4 | 107 | 6.6 | 40 | 30 | 334 | 321 | 592 | 184 | 21.4 | 326 | 332 | 59 | 14 | 0.5 | 125 | 5.1 | 2.4 |
| 5 | 180 | 5.2 | 35 | 25 | 214 | 204 | 548 | 143 | 25 | 367 | 401 | 120 | 10 | 0.6 | 100 | 4.9 | 2.1 |
Case 12: subacute type
| coma | NH3 | PLT | PT | HPT | AST | ALT | LDH | ChE | T.B. | ALP | LAP | rGT | ON | Cr | T.C. | T.P. | Alb |
| 2 | 160 | 22.9 | 21 | 10 | 682 | 666 | 701 | 2.5 | 30.2 | 718 | 261 | 12 | 8 | 0.8 | 82 | 5 | 2.9 |
| 2 | 153 | 20.9 | 20 | 14.5 | 583 | 648 | 635 | 2.4 | 32 | 783 | 322 | 14 | 7.2 | 0.8 | 88 | 5 | 2.9 |
| 1 | 179 | 18.8 | 38 | 17.5 | 353 | 302 | 604 | 2.4 | 25 | 495 | 255 | 5 | 5.8 | 0.7 | 88 | 5 | 3.3 |
| 2 | 190 | 14.8 | 21 | 17 | 296 | 241 | 476 | 6 | 23.8 | 495 | 253 | 32 | 8.1 | 0.7 | 119 | 5 | 3.3 |
| 2 | 160 | 10.2 | 25 | 21 | 264 | 193 | 563 | 8.3 | 22 | 479 | 268 | 31 | 10 | 0.6 | 136 | 5 | 3.2 |
| 2 | 257 | 15.2 | 22 | 16.5 | 345 | 192 | 598 | 8.3 | 20.7 | 415 | 224 | 30 | 10.8 | 0.8 | 135 | 5.2 | 3.4 |
| 2 | 287 | 11.8 | 28 | 21.5 | 319 | 174 | 646 | 7.9 | 18.9 | 399 | 222 | 16 | 10 | 0.7 | 151 | 4.6 | 2.99 |
| 2 | 104 | 3.4 | 10 | 13.5 | 340 | 177 | 730 | 6.4 | 21 | 447 | 214 | 16 | 12.4 | 0.9 | 124 | 4.7 | 2.99 |
| 3 | 93 | 3.4 | 11 | 18 | 244 | 156 | 637 | 6.4 | 22.4 | 447 | 259 | 16 | 14.4 | 0.3 | 124 | 4.8 | 2.9 |
| 5 | 87 | 8.8 | 17.5 | 18.2 | 221 | 147 | 798 | 5.2 | 26.6 | 527 | 262 | 20 | 17.4 | 1 | 116 | 5.2 | 2.8 |
| 5 | 135 | 9.1 | 18 | 17 | 180 | 107 | 942 | 5.1 | 23.8 | 574 | 247 | 15 | 17.1 | 1.1 | 109 | 4.7 | 2.6 |
| 5 | 150 | 5.5 | 10 | 10 | 943 | 285 | 3924 | 4 | 18 | 1453 | 243 | 5 | 22.1 | 4.1 | 81 | 3.8 | 2.4 |
Case 13: subacute type
| coma | NH3 | PLT | PT | HPT | AST | ALT | LDH | ChE | T.B. | ALP | LAP | rGT | UN | Cr | T.C. | T.P. | Alb |
| 3 | 90 | 8 | 29 | 20 | 670 | 845 | 242 | 179 | 0.3 | 559 | 237 | 171 | 5 | 0.4 | 63 | 6.4 | 2.9 |
| 3 | 110 | 6.6 | 17 | 29 | 255 | 391 | 306 | 148 | 15.7 | 512 | 193 | 148 | 16 | 0.8 | 59 | 5.7 | 2.3 |
| 4 | 107 | 5.7 | 16 | 28 | 212 | 233 | 286 | 142 | 26.2 | 522 | 162 | 106 | 14 | 0.5 | 56 | 5.9 | 2.2 |
| 5 | 180 | 5.5 | 15 | 30 | 159 | 140 | 244 | 111 | 28.9 | 687 | 298 | 189 | 10 | 0.6 | 56 | 5.4 | 2.1 |
Case 14: subacute type
| coma | NH3 | PLT | PT | HPT | AST | ALT | LDH | ChE | T.B. | ALP | LAP | rGT | UN | Cr | T.C. | T.P. | Alb |
| 2 | 66 | 10.5 | 30 | 38 | 102 | 94 | 351 | 200 | 36.1 | 638 | 340 | 81 | 25 | 2.1 | 79 | 6.6 | 2.8 |
| 2 | 50 | 10.9 | 29 | 27 | 77 | 86 | 366 | 216 | 30.1 | 591 | 342 | 82 | 19 | 1.8 | 79 | 5.7 | 2.6 |
| 2 | 40 | 10.5 | 60 | 66 | 59 | 63 | 346 | 204 | 27.4 | 453 | 338 | 72 | 18 | 1.5 | 85 | 5.2 | 2.4 |
| 2 | 30 | 11.6 | 63 | 31 | 37 | 40 | 360 | 322 | 22.8 | 390 | 282 | 52 | 25 | 1.7 | 85 | 5 | 2.3 |
| 2 | 74 | 11 | 50 | 40 | 53 | 57 | 571 | 319 | 25.2 | 431 | 328 | 91 | 21 | 1.6 | 100 | 5.1 | 2.4 |
| 2 | 42 | 9.2 | 60 | 65 | 37 | 29 | 348 | 260 | 21 | 367 | 251 | 60 | 22 | 2 | 112 | 5 | 2.7 |
| 2 | 54 | 8.9 | 50 | 39 | 36 | 29 | 303 | 316 | 22.6 | 335 | 237 | 40 | 22 | 1.9 | 100 | 5.5 | 2.9 |
| 2 | 55 | 9 | 50 | 40 | 43 | 28 | 361 | 336 | 31.3 | 448 | 209 | 54 | 21 | 1.8 | 102 | 6.1 | 3.4 |
| 2 | 64 | 9 | 35 | 30 | 28 | 22 | 283 | 337 | 16.5 | 255 | 199 | 31 | 20 | 1.7 | 95 | 5.6 | 3.4 |
| 2 | 65 | 9 | 40 | 30 | 26 | 21 | 309 | 319 | 15.4 | 303 | 231 | 36 | 21 | 1.6 | 100 | 6.2 | 3.5 |
| 2 | 65 | 9.9 | 33 | 25 | 28 | 22 | 267 | 347 | 15.8 | 479 | 278 | 47 | 23 | 1.3 | 131 | 5.9 | 3.6 |
| 2 | 66 | 7.7 | 55 | 54 | 31 | 18 | 262 | 262 | 19.9 | 287 | 214 | 43 | 20 | 1.2 | 99 | 5 | 2.9 |
| 2 | 54 | 9 | 26 | 25 | 35 | 34 | 246 | 332 | 22.5 | 149 | 246 | 50 | 17.8 | 1.2 | 100 | 5.7 | 3.3 |
| 2 | 76 | 8.7 | 30 | 24 | 40 | 34 | 234 | 300 | 24.4 | 367 | 243 | 40 | 18 | 1.3 | 95 | 6.1 | 3.8 |
| 2 | 66 | 9.1 | 23 | 25 | 38 | 17 | 213 | 310 | 26.9 | 367 | 249 | 46 | 19 | 1.3 | 100 | 6.2 | 3.7 |
| 4 | 54 | 9.2 | 30 | 34 | 29 | 7 | 238 | 326 | 22.6 | 335 | 225 | 35 | 20 | 1.2 | 129 | 6.5 | 3.9 |
| 5 | 88 | 8.9 | 19 | 15 | 31 | 12 | 183 | 204 | 23.3 | 271 | 196 | 40 | 20 | 1.4 | 110 | 5.2 | 3.1 |
Case 15: subacute type
| coma | NH3 | PLT | PT | HPT | AST | ALT | LDH | ChE | T.B. | ALP | LAP | rGT | UN | Cr | T.C. | T.P. | Alb |
| 4 | 202 | 0.8 | 53 | 48 | 21 | 10 | 334 | 103 | 23.5 | 1357 | 248 | 11 | 102 | 4.5 | 55 | 5.4 | 2.3 |
| 2 | 85 | 1.3 | 45 | 40 | 28 | 7 | 510 | 110 | 27.9 | 1581 | 263 | 10 | 111 | 5.5 | 47 | 5.6 | 2.1 |
| 2 | 64 | 1.3 | 48 | 45 | 33 | 10 | 331 | 113 | 33.7 | 1357 | 277 | 15 | 131 | 3.7 | 38 | 5.7 | 2.2 |
| 2 | 70 | 1 | 40 | 35 | 33 | 15 | 236 | 65 | 37 | 1038 | 277 | 10 | 133 | 4.2 | 40 | 6 | 2.3 |
| 2 | 84 | 1.8 | 45 | 40 | 40 | 16 | 250 | 124 | 38.5 | 1117 | 281 | 4 | 106 | 4.2 | 39 | 5.9 | 2.2 |
| 2 | 56 | 1.9 | 45 | 40 | 38 | 10 | 280 | 133 | 44 | 1197 | 295 | 3 | 127 | 3.7 | 41 | 6.3 | 2.5 |
| 2 | 26 | 3.5 | 68 | 50 | 33 | 16 | 264 | 270 | 35.6 | 1117 | 270 | 5 | 111 | 2.6 | 60 | 6.6 | 2.6 |
| 3 | 30 | 3.8 | 40 | 35 | 29 | 12 | 298 | 207 | 31.9 | 862 | 262 | 3 | 119 | 3.5 | 80 | 6 | 2.5 |
| 5 | 214 | 2.6 | 30 | 25 | 279 | 89 | 1425 | 240 | 28.5 | 1038 | 249 | 6 | 112 | 4.3 | 70 | 5.9 | 2.2 |
Case 16: Acute on chronic
| coma | NH3 | PLT | PT | HPT | AST | ALT | LDH | ChE | T.B. | ALP | LAP | rGT | UN | Cr | T.C. | T.P. | Alb |
| 2 | 117 | 5.6 | 12.5 | 10 | 1644 | 765 | 1079 | 32 | 35.7 | 1676 | 268 | 18 | 5 | 0.4 | 44 | 7.7 | 3.1 |
| 2 | 138 | 6.4 | 12 | 10 | 1105 | 575 | 674 | 48 | 37.3 | 1309 | 296 | 17 | 16 | 0.8 | 54 | 8 | 3.2 |
| 2 | 107 | 9.3 | 9.9 | 8 | 488 | 367 | 668 | 44 | 36.1 | 1373 | 230 | 16 | 14 | 0.5 | 41 | 6.2 | 3.1 |
| 5 | 180 | 8.4 | 16.5 | 15 | 415 | 219 | 1182 | 48 | 26.5 | 942 | 164 | 7 | 10 | 0.6 | 80 | 5.3 | 3 |
Case 17: Acute on chronic
| coma | NH3 | PLT | PT | HPT | AST | ALT | LDH | ChE | T.B. | ALP | LAP | rGT | UN | Cr | T.C. | T.P. | Alb |
| 0 | 30 | 6.5 | 46 | 31 | 647 | 540 | 644 | 167 | 18.7 | 479 | 375 | 63 | 15 | 1.1 | 117 | 5.4 | 2.9 |
| 2 | 60 | 6.6 | 40 | 30 | 334 | 321 | 592 | 184 | 21.4 | 399 | 332 | 59 | 23 | 1.3 | 125 | 5.1 | 2.6 |
| 2 | 46 | 5.2 | 43 | 30 | 214 | 204 | 548 | 154 | 21 | 335 | 299 | 50 | 30 | 1.4 | 100 | 4.9 | 2.6 |
| 2 | 48 | 5.5 | 51 | 31 | 338 | 218 | 633 | 250 | 21.3 | 383 | 324 | 46 | 30 | 1.3 | 123 | 5.5 | 2.9 |
| 2 | 66 | 5.4 | 53 | 40 | 370 | 225 | 650 | 254 | 20.4 | 351 | 289 | 41 | 29 | 1.3 | 110 | 5.3 | 2.7 |
| 2 | 67 | 7.8 | 50 | 41 | 238 | 174 | 606 | 274 | 19.6 | 367 | 297 | 42 | 29 | 1.3 | 136 | 5.2 | 2.7 |
| 2 | 30 | 6 | 64 | 62 | 98 | 77 | 456 | 426 | 11.6 | 415 | 239 | 32 | 32 | 1.3 | 160 | 5.6 | 3.2 |
| 2 | 72 | 9.5 | 68 | 50 | 111 | 82 | 432 | 471 | 12.6 | 447 | 258 | 45 | 36 | 1.2 | 170 | 5.9 | 3.3 |
| 2 | 48 | 6.7 | 51 | 54 | 201 | 128 | 513 | 412 | 14.4 | 447 | 299 | 54 | 21 | 1.2 | 202 | 5.7 | 3 |
| 2 | 46 | 5.2 | 61 | 57 | 172 | 124 | 542 | 374 | 16.9 | 447 | 283 | 48 | 28 | 1.2 | 174 | 5.2 | 2.7 |
| 2 | 40 | 5.3 | 61 | 49 | 150 | 88 | 537 | 360 | 17.2 | 335 | 221 | 29 | 29 | 1.2 | 148 | 5.2 | 2.7 |
| 2 | 48 | 5.9 | 65 | 50 | 102 | 76 | 469 | 378 | 23 | 399 | 287 | 40 | 39 | 1.1 | 213 | 5.7 | 3.1 |
| 2 | 50 | 5.5 | 55 | 54 | 199 | 121 | 451 | 363 | 30 | 479 | 303 | 47 | 34 | 1.1 | 210 | 5.7 | 3 |
| 2 | 48 | 4.7 | 55 | 58 | 123 | 73 | 386 | 378 | 24.4 | 351 | 233 | 31 | 34 | 1.1 | 144 | 5.5 | 3.1 |
| 2 | 50 | 6.2 | 50 | 45 | 141 | 94 | 427 | 407 | 30.1 | 431 | 267 | 38 | 31 | 1.1 | 170 | 5.9 | 3.1 |
| 2 | 52 | 4.6 | 56 | 53 | 99 | 77 | 386 | 397 | 26.9 | 463 | 277 | 39 | 25 | 1.1 | 169 | 5.6 | 3.1 |
| 2 | 34 | 5.1 | 60 | 51 | 164 | 105 | 634 | 370 | 37.6 | 495 | 318 | 53 | 39 | 1.1 | 168 | 5.7 | 2.8 |
| 3 | 70 | 6.2 | 58 | 46 | 140 | 81 | 580 | 349 | 34.4 | 511 | 326 | 48 | 50 | 1.3 | 151 | 5.3 | 2.8 |
| 3 | 58 | 4.9 | 57 | 46 | 137 | 88 | 607 | 344 | 37.4 | 511 | 334 | 47 | 66 | 1.4 | 157 | 5.2 | 2.6 |
| 3 | 70 | 6 | 48 | 41 | 121 | 87 | 678 | 353 | 35.3 | 671 | 369 | 51 | 67 | 1.3 | 156 | 5.4 | 2.6 |
| 3 | 75 | 3.8 | 36 | 31 | 367 | 132 | 1344 | 324 | 32.4 | 703 | 382 | 61 | 99 | 2.3 | 119 | 5.1 | 2.6 |
Case 18: Acute on chronic
| coma | NH3 | PLT | PT | HPT | AST | ALT | LDH | ChE | T.B. | ALP | LAP | rGT | UN | Cr | T.C. | T.P. | Alb |
| 2 | 108 | 7.6 | 37 | 38 | 104 | 19 | 438 | 101 | 32.2 | 1277 | 460 | 503 | 73.6 | 3.1 | 160 | 4.5 | 2.1 |
| 2 | 90 | 14.2 | 35 | 35 | 89 | 22 | 531 | 95 | 30.4 | 1357 | 470 | 407 | 103 | 4.3 | 152 | 5.2 | 2.7 |
| 1 | 68 | 10 | 36 | 35 | 71 | 26 | 508 | 113 | 38.4 | 1245 | 450 | 461 | 106 | 3.4 | 150 | 5 | 2.5 |
| 2 | 62 | 6 | 36 | 32 | 40 | 25 | 495 | 128 | 34 | 1293 | 479 | 378 | 110 | 4.1 | 149 | 5.4 | 3.1 |
| 3 | 48 | 7 | 35 | 40 | 31 | 24 | 336 | 132 | 33.9 | 1197 | 420 | 320 | 113 | 2.6 | 145 | 5 | 2.6 |
| 3 | 130 | 6.2 | 43 | 50 | 40 | 35 | 350 | 150 | 34.8 | 1117 | 359 | 258 | 137 | 4 | 160 | 5.8 | 3.9 |
| 3 | 124 | 9.5 | 40 | 45 | 42 | 30 | 345 | 220 | 33.3 | 894 | 320 | 223 | 165 | 3.4 | 150 | 5.9 | 3 |
| 3 | 72 | 9.1 | 27 | 35 | 42 | 20 | 343 | 294 | 20.8 | 686 | 279 | 159 | 194 | 4 | 160 | 5.8 | 3.5 |
| 3 | 60 | 10.9 | 40 | 50 | 33 | 25 | 479 | 260 | 14.8 | 878 | 334 | 199 | 260 | 4.9 | 155 | 7 | 4.8 |
| 4 | 96 | 4.9 | 37 | 41 | 22 | 22 | 363 | 251 | 15 | 798 | 320 | 200 | 294 | 5.1 | 163 | 7.4 | 5.1 |
| 5 | 100 | 2.9 | 34 | 38 | 26 | 28 | 592 | 494 | 16 | 766 | 309 | 199 | 324 | 6 | 160 | 7 | 4.5 |
| 5 | 138 | 2.3 | 30 | 28 | 36 | 40 | 550 | 450 | 17 | 846 | 320 | 220 | 378 | 7.8 | 150 | 6.5 | 4.1 |
Case 19: Acute on chronic
Table 5: The data of 7 dead cases of fluminant hepatitis used for examination.
This unit space was made by the data of physically normal person. “MD=1” is the center in unit space. When MD increases, it is meant that an object leaves from the physically normal person who is unit space. Therefore, change of MD was compared with a change of clinical data every case and was considered. By MD which was a unitary statistic, pathologic aggravation and grasp of the improvement were considered. In addition, the data of 30 physically normal people and 19 patients were collected in anonymous form. The patient privacy is protected. In addition, t-test was used for significant difference examination. “The MT system 1, MT method” of the software made in oken company was used for a calculation of MD.
Results
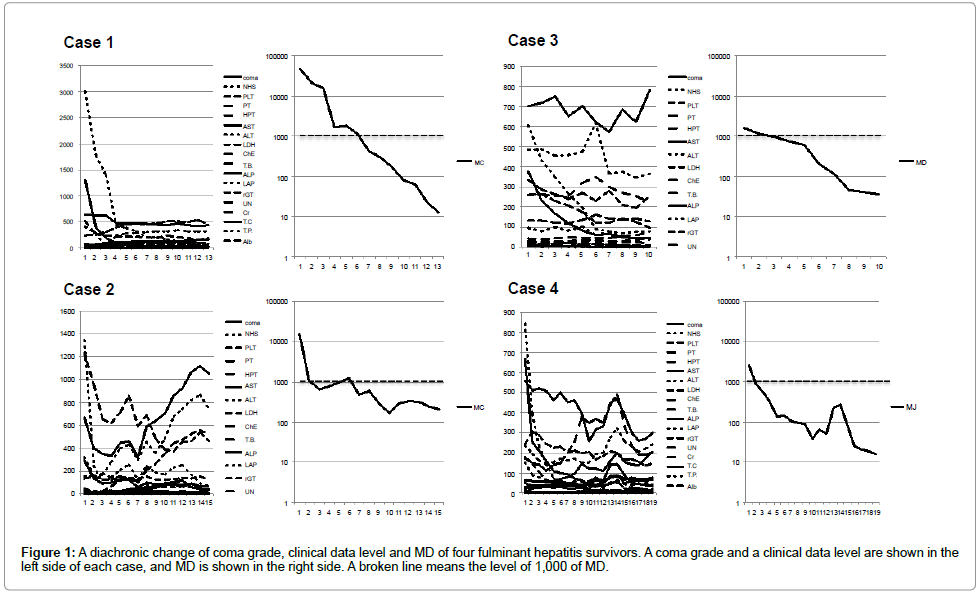
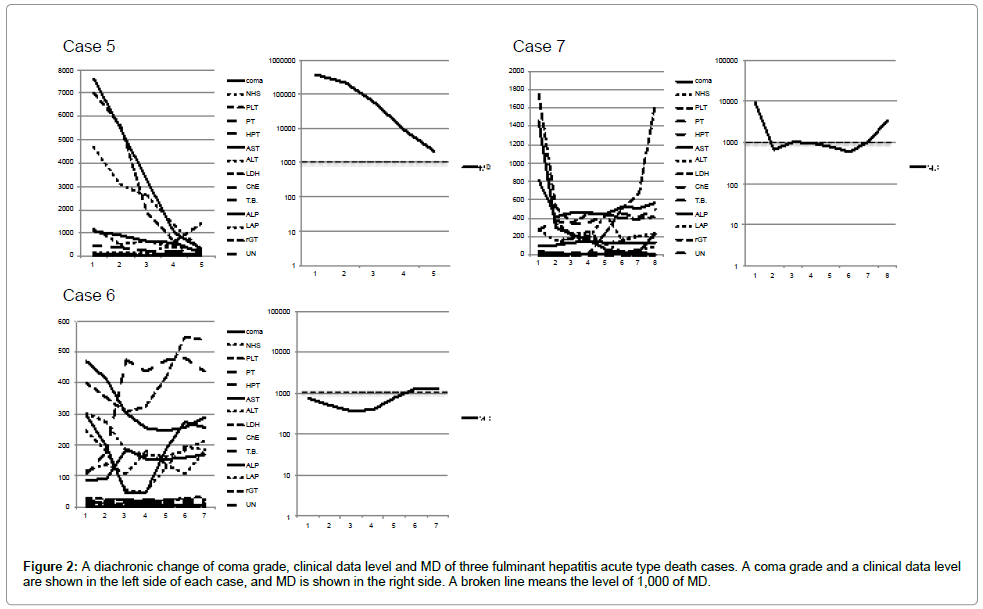
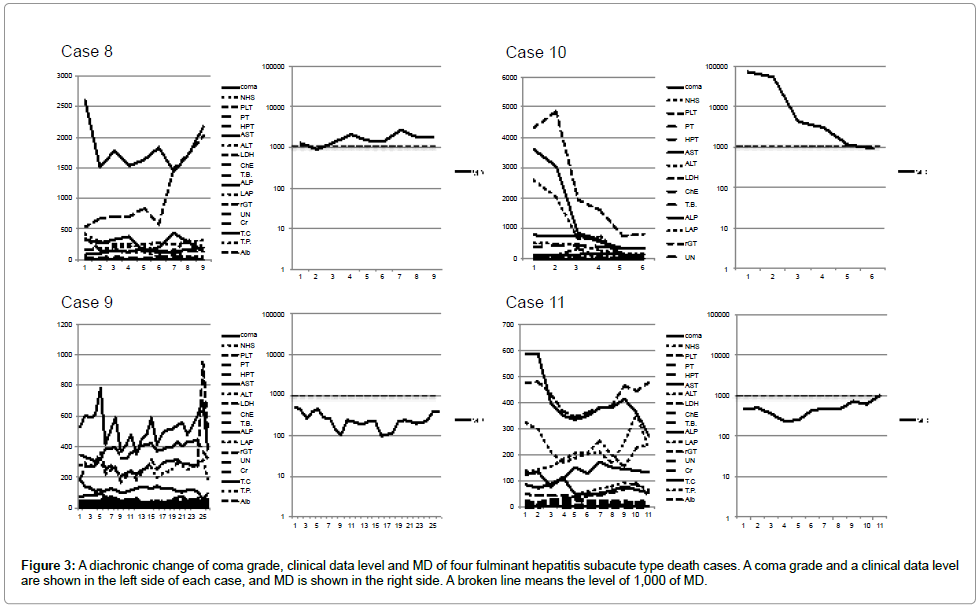
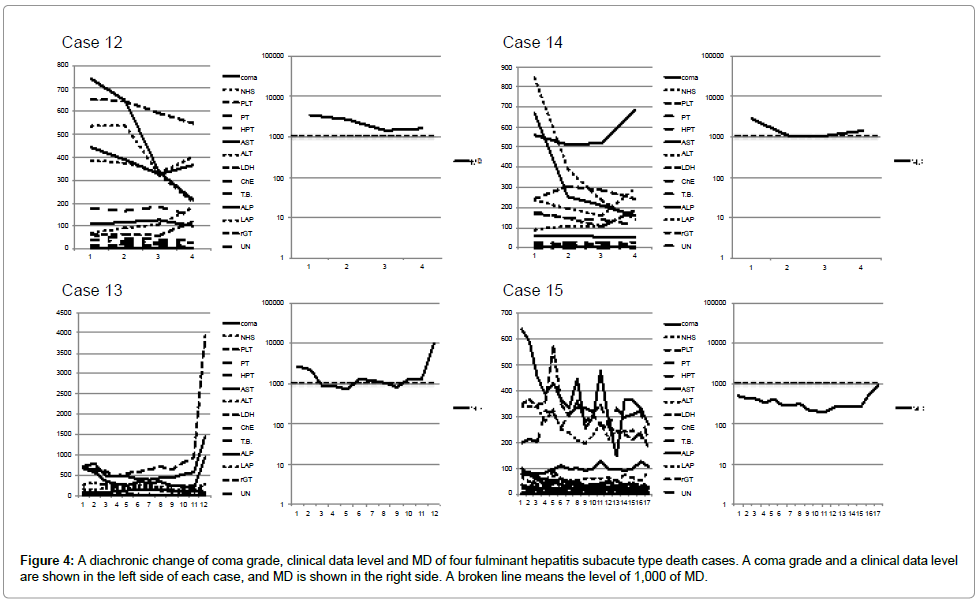
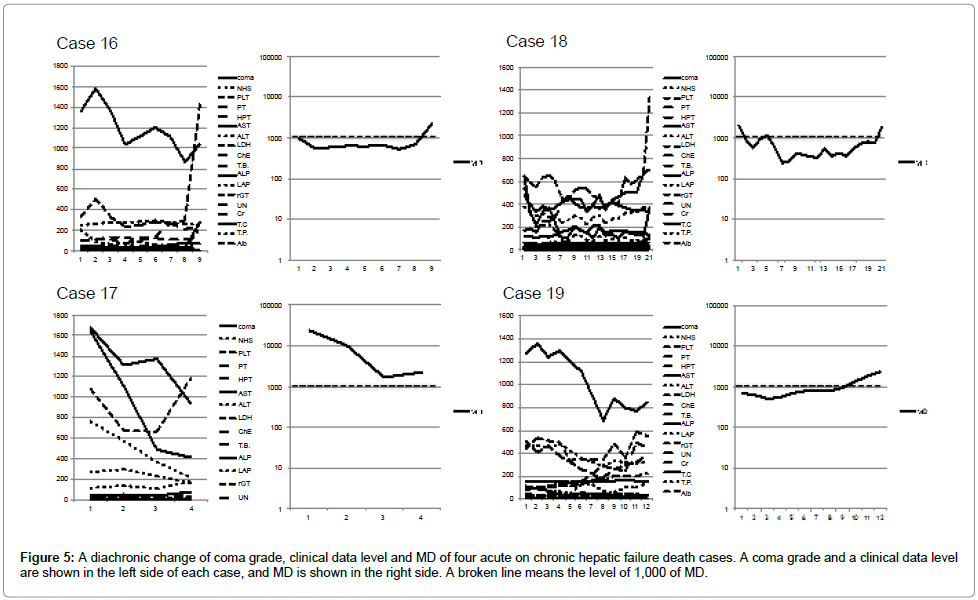
The data of 19 cases at the time of hospital discharges or death were shown in Figures 1-5. The change of the data of 18 items was shown in the figure left side. The logarithmic change of MD was shown in the figure right side.
As shown in Figure 1, MD of the early period of onset of four fulminant hepatitis survivors was more than several thousand. With case 1 and 4, the data level of 18 items decreased generally. Data fluctuated with case 2 and 3 complicatedly up and down, but MD decreased smoothly. And MD approached to the unit space according to improvement of hepatic failure of the patient.
Three death cases of fulminant hepatitis acute type were shown in Figure 2. With case 5, the data of 18 items improved by treatment, and MD reflected this improvement and as a result MD decreased. Just before the death, MD level was 1,318 amd this MD meant a terminal liver disease and the patient died by renal failure. Case 6 and 7 improved the data of 18 items by an effect of treatment once. However, the data turned worse with progress of hepatic failure and, as a result, MD level showed more than 1,000 again, and the patients died by hepatic failure.
Eight death cases of fulminant hepatitis subacute type were shown in Figures 3 and 4. Case 10, 12 and 14 reflected curative effect, and the data of 18 items were improved. However, MD level of case 10 decreased to 906 just before the death, but the patient died by renal failure not hepatic failure. In addition, MD level of case 12 was 1,571, and MD level of case 14 was 1,385. Their MD showed terminal level of 1,000 or more and died by hepatic failure. Data of other five cases turned worse according as pathologic aggravation. It was reflected on increase of MD, and the patient died.
Four death cases of acute on chronic hepatic failure were shown in Figure 5. In these four cases, 18 items accept a complicated change. On the other hand, MD decreased by treatment slightly once. However, the disease turned worse, and MD level increased about 2,000 and the patient died.
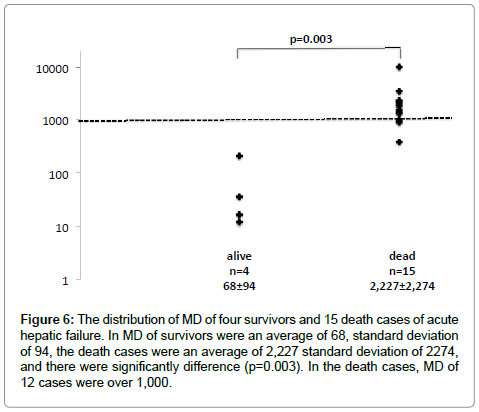
The MD level was divided into survival case and death case, and a logarithm of MD was shown in Figure 6. MD level of four survivors decreases to an average of 68, standard deviation of 94 at the time of hospital discharge and was normalized afterwards. On the other hand, MD level in 15 death was an average of 2,227, standard deviation of 2,274. This MD level was significantly higher than survivors by t-test (p=0.003), and MD level of 12 cases were more than 1,000. Three MD decreased with progress, but in the death of three cases, MD level of case 9 increased to 390, MD level of case 15 to 922. The change of these MD reflected pathologic aggravation. In the death, MD level of case 10 decreased to 906 from 7,173, but the patient died by renal failure not hepatic failure.
Figure 6: The distribution of MD of four survivors and 15 death cases of acute hepatic failure. In MD of survivors were an average of 68, standard deviation of 94, the death cases were an average of 2,227 standard deviation of 2274, and there were significantly difference (p=0.003). In the death cases, MD of 12 cases were over 1,000.
Consideration
As for the characteristic of MT system, the unit space is made using the data of physically normal person. MD for this unit space is calculated by the data of patient “individual”, not statistical “group”, and is evaluated, and as a results, “individual changes” of patient are judged as a unitary statistic. In addition, the correlation of data of patient individual is examined in MT system. We examined change of MD in the liver disease until now. And we reported about increase of MD showed pathologic aggravation, and decrease of MD showed pathologic improvement [7,8]. In addition, MD level more than 1,000 means terminal liver diseases. And MD level more than 1,000 became the index of liver transplantation [9].
In this study, clinical data fluctuated complicatedly by clinical course, and a judgment of improvement or aggravation of these diseases are difficult. Each clinical data are unified into MD, and evaluate MD. As a result, pathologic grasp becomes easy using a common evaluation standard for doctor. MD decreased with this four survivors immediately, and the condition of a patient was improved. In the case of 5, 10, 17, MD level decreased, but it was still more than 1,000 at death time. In addition, case 5 and 10 died by renal failure, and case 17 died by gastrointestinal bleeding, not hepatic failure.
The unit space of MT system was defined each time. This 18 items were for the evaluations of hepatic failure. The hepatic failure of case 5,10,17 was improved, however, these cause of death was renal failure and gastrointestinal bleeding, not hepatic failure. Renal failure and gastrointestinal bleeding were hard to evaluate in these 18 items, as a results, the evaluation of MD was low grade. For the renal failure, only two items of UN and Cr are insufficient. The datas such as quantity of glomerulus filtration, volume of urine or edema increase may becomes a more accurate index. For the gastrointestinal bleeding, the much frequent endoscopy is difficult, so datas such as blood UN level, an occult bleeding reaction or melena will be necessary in future.
The clinical datas of 13 death cases was complicated, and pathologic grasp was difficult. However, pathologic grasp becomed easy with one numerical value by unifying those clinical datas into MD. By treatment, MD decreased 13 cases temporarily, however MD gradually increased with pathologic aggravation and the patients died.
When MD unifying clinical datas as above is calculated, pathologic grasp to change complicatedly becomes easy. And the evaluation standard that is common to the diagnosis of the doctor is given.
Conclusion
“Individual changes” are evaluated as a unitary statistic in MD. Using MD from the unit space of physically normal person, complicated pathologic grasp of acute hepatic failure becomes much easy.
References
- Taguchi G (2005) Function and functionality 46. Classification by the MTA method. Standardization and Quality Control 58: 57-64.
- Kanetaka H (1997) Judgment of the medical examination using Mahalanobis distance. Quality Engineering 5: 25-44.
- Makajima H, Takada K, Yano H, Takagi I, Shibamoto Y, et al. (1999) [Predictive evaluation and efficient management of medical examinations using Mahalanobis Taguchi System Method]. Nihon Koshu Eisei Zasshi 46: 351-363.
- Nakajima H, Takada K, Yano H (2004) Forecasting future health from existing medical examination results using the MTS. Taguchi’s quality engineering handbook, Taguchi G (eds.). John Wiley & Sons, New Jersey 1277-1287.
- Nakajima H, Takada K, Yano H (2004) Forecasting of future health and cost reduction of medical examination using MT method. Quality Engineering 12: 63-72.
- Nakajima H, Takada K, Yano H (1999) Forecasting of the future health from existing medical examination results using Mahalanobis-Taguchi system. Quality Engineering 7: 49-57.
- Nakajima H, Yano K, Takada K (2004) Diseases state evaluation and diagnosis by the change of Mahalanobis distance for the various types of liver diseases. Quality Engineering 12: 51-58.
- Nakajima H, Yano K, Komiya S (2004) Computerization of medical treatment and practice of evidence-based medicine by the Mahalanobis-Taguchi methods. Quality Engineering 12: 50-57.
- Nakajima H, Yano K, Takagi I (2006) The examination of forecast of fulminant hepatitis for liver transplantation using the Mahalanobis-Taguchi system. Quality Engineering 14: 58-63.
- Nakajima H, Yano K, Uetake S, Takagi I (2012) Diagnosis of liver diseases by classification of laboratory signal factor pattern findings with the Mahalanobis·Taguchi Adjoint method. Nihon Shokakibyo Gakkai Zasshi 109: 198-210.
Relevant Topics
- Addiction
- Adolescence
- Children Care
- Communicable Diseases
- Community Occupational Medicine
- Disorders and Treatments
- Education
- Infections
- Mental Health Education
- Mortality Rate
- Nutrition Education
- Occupational Therapy Education
- Population Health
- Prevalence
- Sexual Violence
- Social & Preventive Medicine
- Women's Healthcare
Recommended Journals
Article Tools
Article Usage
- Total views: 15710
- [From(publication date):
July-2013 - Nov 19, 2025] - Breakdown by view type
- HTML page views : 10952
- PDF downloads : 4758