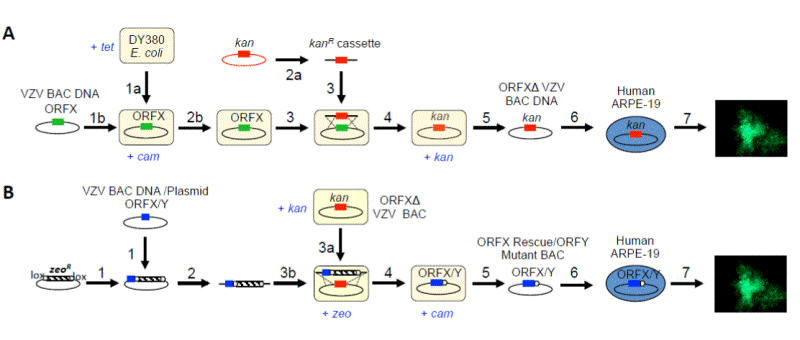
DY380 are made to be electrocompetent (E.C.) (1a) for VZV BAC DNA transformation (1b). Next, a kanamycin resistant gene is PCR amplified by primers containing 40-bp sequences homologous to the flanking regions of the gene or region of interest (ORFX) in VZV to create the kanamycin resistance cassette (2a). In order to generate a deletion mutant clone (ORFXΔ VZV), DY380 E. coli carrying WT VZV BAC undergo E.C. cell preparation with recombinase system activated (2b). The kanamycin resistance cassette is then transformed into the E.C. DY380 harboring WT VZV BAC (3). Upon homologous recombination, ORFX will be replaced by the kanamycin resistant gene, generating the VZV ORFXΔ mutant BAC clone (4). The deletion clone is then verified by PCR and sensitivity to antibiotics, and extracted via BAC Maxipreparation (5).The mutant BAC is then chemically transfected into human ARPE-19 cells (6) and grown for mutant analysis (7). B. Generation of ORF rescue/ mutant VZV virus. A plasmid containing a zeocin resistant gene flanked by loxP sites is used for cloning of either ORFX (for rescue) or ORFY (for introduction of new gene or mutated ORFX) (1). The ORFX/Y flanked by the zeocin resistant gene is PCR amplified (2), conferring 40-bp homology to the regions flanking the kanamycin resistance gene in the VZV ORFXΔ mutant BAC. DY380 harboring VZV ORFXΔ mutant BAC are made electrocompetent and its recombination system activated (3a) for transformation of rescue cassette and cre recombinase (3b). Upon homologous recombination (4), a VZV ORFX/Y rescue BAC is generated. Furthermore, when cre recombinase is transformed, the zeocin marker is excised, leaving little foreign DNA remaining in the BAC. After PCR verification and extraction of the rescue BAC via Maxipreparation (5), the ORFX Rescue/ORFY Mutant BAC DNA is chemically transfected into human ARPE-19 cells (6). The virus that results is then grown and analyzed for comparison to WT VZV (7).
*Images adapted from Dulal et al.